Run and Long Run Equilibrium
1) The data in the above table indicate that the economy will be in a short-run macroeconomic equilibrium at a price level
A) between 130 and 121.
B) between 119 and 111.
C) of 120.
D) of 110.
Answer: B
2) From the data in the above table, when the economy is at its short -run equilibrium, if aggregate
demand does not change, then as time passes the
A) short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
Answer: B

3) The data in the above table show that the economy will be in a short -run macroeconomic
equilibrium at a price level of
A) 90.
B) 110.
C) 100.
D) 120.
Answer: D
4) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120,
A) the unemployment rate is below its natural rate.
B) the unemployment rate is above its natural rate.
C) money wages rates will rise in the future.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward in the future.
Answer: B
5) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, the economy
A) is in a long-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
B) has an inflationary gap.
C) has a recessionary gap.
D) will have falling money wage rates sometime in the future.
Answer: C
6) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, if aggregate demand does not change then the
A) money wage rate will rise in the future.
B) money wage rate will fall in the future.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
Answer: B
7) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, if aggregate demand does not change then the
A) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
Answer: A
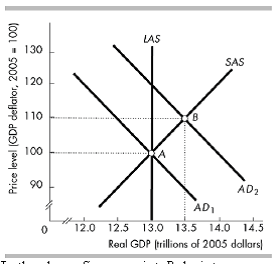
8) In the above figure, point B depicts
A) an inflationary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
B) an inflationary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
C) a recessionary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
D) a recessionary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
Answer: A
9) In the above figure, real GDP at full employment is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: A
10) In the above figure, the aggregate demand curve is AD2, so the short-run equilibrium level of
real GDP is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: B
11) In the above figure, the aggregate demand curve is AD2, so the long-run equilibrium level of real GDP is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: A
12) In the above figure, the shift from AD1 to AD2 might have been the result of
A) an increase in government expenditure.
B) a decrease in taxes.
C) an increase in the quantity of money.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
Answer: D
13) Higher resource prices shift the
A) long-run aggregate supply curve leftward, decreasing real GDP and increasing potential GDP.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve leftward, raising the price level and decreasing potential GDP.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve leftward, raising the price level and decreasing real GDP so it is less than potential GDP.
D) short-run aggregate supply curve rightward, raising the price level and decreasing real GDP so it is less than potential GDP.
Answer: C
14) Suppose that the economy begins at a long-run equilibrium. Which of the following raises the
price level and decrease real GDP in the short run?
A) a decrease in the quantity of money
B) an increase in the price of oil that decreases aggregate supply
C) an increase in the stock of capital that increases aggregate supply
D) an increase in government expenditures
Answer: B
15) A decrease in short-run aggregate supply ________ the equilibrium price level and ________ the equilibrium quantity of real GDP.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
Answer: B
16) In the short run, a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve ________ real GDP and ________ the price level.
A) decreases; lowers
B) increases; raises
C) decreases; raises
D) increases; lowers
Answer: D
17) In the short run, a supply shock that shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward ________ real GDP and ________ the price level.
A) increases; raises
B) decreases; raises
C) increases; lowers
D) decreases; lowers
Answer: B
18) Assume the economy is at long run equilibrium and oil prices rise. As a result, the ________ shifts ________.
A) AD; rightward
B) AD; leftward
C) SAS; rightward
D) SAS; leftward
Answer: D
19) In the short-run, a rise in the money wage rate leads to
A) an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
C) an increase in the price level, but no change in real GDP.
D) no change in the price level, but an increase in real GDP.
Answer: B
20) Stagflation is the combination of
A) inflation and increasing real GDP.
B) deflation and recession.
C) inflation and recession.
D) deflation with increasing real GDP.
Answer: C
A) between 130 and 121.
B) between 119 and 111.
C) of 120.
D) of 110.
Answer: B
2) From the data in the above table, when the economy is at its short -run equilibrium, if aggregate
demand does not change, then as time passes the
A) short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
Answer: B

3) The data in the above table show that the economy will be in a short -run macroeconomic
equilibrium at a price level of
A) 90.
B) 110.
C) 100.
D) 120.
Answer: D
4) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120,
A) the unemployment rate is below its natural rate.
B) the unemployment rate is above its natural rate.
C) money wages rates will rise in the future.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward in the future.
Answer: B
5) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, the economy
A) is in a long-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
B) has an inflationary gap.
C) has a recessionary gap.
D) will have falling money wage rates sometime in the future.
Answer: C
6) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, if aggregate demand does not change then the
A) money wage rate will rise in the future.
B) money wage rate will fall in the future.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
Answer: B
7) The data in the above table show that when the price level is 120, if aggregate demand does not change then the
A) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift rightward.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve will shift leftward.
Answer: A

8) In the above figure, point B depicts
A) an inflationary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
B) an inflationary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
C) a recessionary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
D) a recessionary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
Answer: A
9) In the above figure, real GDP at full employment is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: A
10) In the above figure, the aggregate demand curve is AD2, so the short-run equilibrium level of
real GDP is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: B
11) In the above figure, the aggregate demand curve is AD2, so the long-run equilibrium level of real GDP is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
Answer: A
12) In the above figure, the shift from AD1 to AD2 might have been the result of
A) an increase in government expenditure.
B) a decrease in taxes.
C) an increase in the quantity of money.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
Answer: D
13) Higher resource prices shift the
A) long-run aggregate supply curve leftward, decreasing real GDP and increasing potential GDP.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve leftward, raising the price level and decreasing potential GDP.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve leftward, raising the price level and decreasing real GDP so it is less than potential GDP.
D) short-run aggregate supply curve rightward, raising the price level and decreasing real GDP so it is less than potential GDP.
Answer: C
14) Suppose that the economy begins at a long-run equilibrium. Which of the following raises the
price level and decrease real GDP in the short run?
A) a decrease in the quantity of money
B) an increase in the price of oil that decreases aggregate supply
C) an increase in the stock of capital that increases aggregate supply
D) an increase in government expenditures
Answer: B
15) A decrease in short-run aggregate supply ________ the equilibrium price level and ________ the equilibrium quantity of real GDP.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
Answer: B
16) In the short run, a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve ________ real GDP and ________ the price level.
A) decreases; lowers
B) increases; raises
C) decreases; raises
D) increases; lowers
Answer: D
17) In the short run, a supply shock that shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward ________ real GDP and ________ the price level.
A) increases; raises
B) decreases; raises
C) increases; lowers
D) decreases; lowers
Answer: B
18) Assume the economy is at long run equilibrium and oil prices rise. As a result, the ________ shifts ________.
A) AD; rightward
B) AD; leftward
C) SAS; rightward
D) SAS; leftward
Answer: D
19) In the short-run, a rise in the money wage rate leads to
A) an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
C) an increase in the price level, but no change in real GDP.
D) no change in the price level, but an increase in real GDP.
Answer: B
20) Stagflation is the combination of
A) inflation and increasing real GDP.
B) deflation and recession.
C) inflation and recession.
D) deflation with increasing real GDP.
Answer: C

Comments
Post a Comment